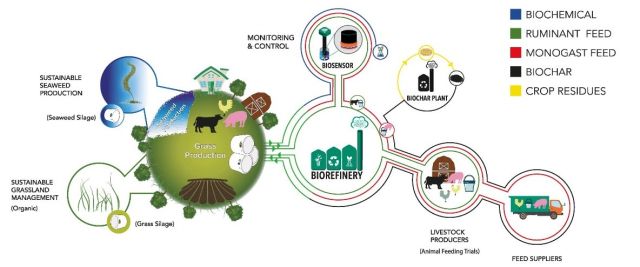
Climate change and the increasing demand for animal foods are major challenges for the earth and humanity. Agriculture is directly affected by these developments, but it can also be a key technology for solving these problems. Therefore, the four-year European “farm4more” project is investigating strategies and technologies to reduce climate change. Additional research is being carried out into ways to provide regional protein supplies to farm animals. Great attention is also paid to the systems approach of organic farming. In organic farming, clover grass is often grown and silage is produced as part of crop rotation. After the fermentation process, this silage can be pressed to produce a protein concentrate from the pressed juice. This concentrate can be used in feeding pigs and poultry to reduce feed imports.
Due to the very high adsorption capacity of coal, reduced emissions can occur when used for feeding purposes. Therefore, as part of the project, a pilot plant will be put into operation to produce coal from hardwood through pyrolysis. If coal meets stricter quality guidelines, it can also be used as animal feed and could thus contribute to reducing emissions.
These approaches and possible effects are being tested and verified at the HBLFA Raumberg-Gumpenstein on fattening poultry and dairy cows as part of the EU Life project.