This procedure is also used for sulfur fertilization in grassland and arable land. The desulfurization of fuels and flue gases in recent decades has resulted in a significant reduction in atmospheric sulfur inputs into Austria's soils. Since a sulfur deficiency affects a plant's entire nitrogen cycle, appropriate sulfur fertilization in the form of elemental sulfur in powder form is often used. In order to save having to spread the fertilizer using a fertilizer spreader, it can also be stirred directly into the slurry pit or the slurry tank - this was the recommendation of many trading companies that sell elemental sulfur or similar products.
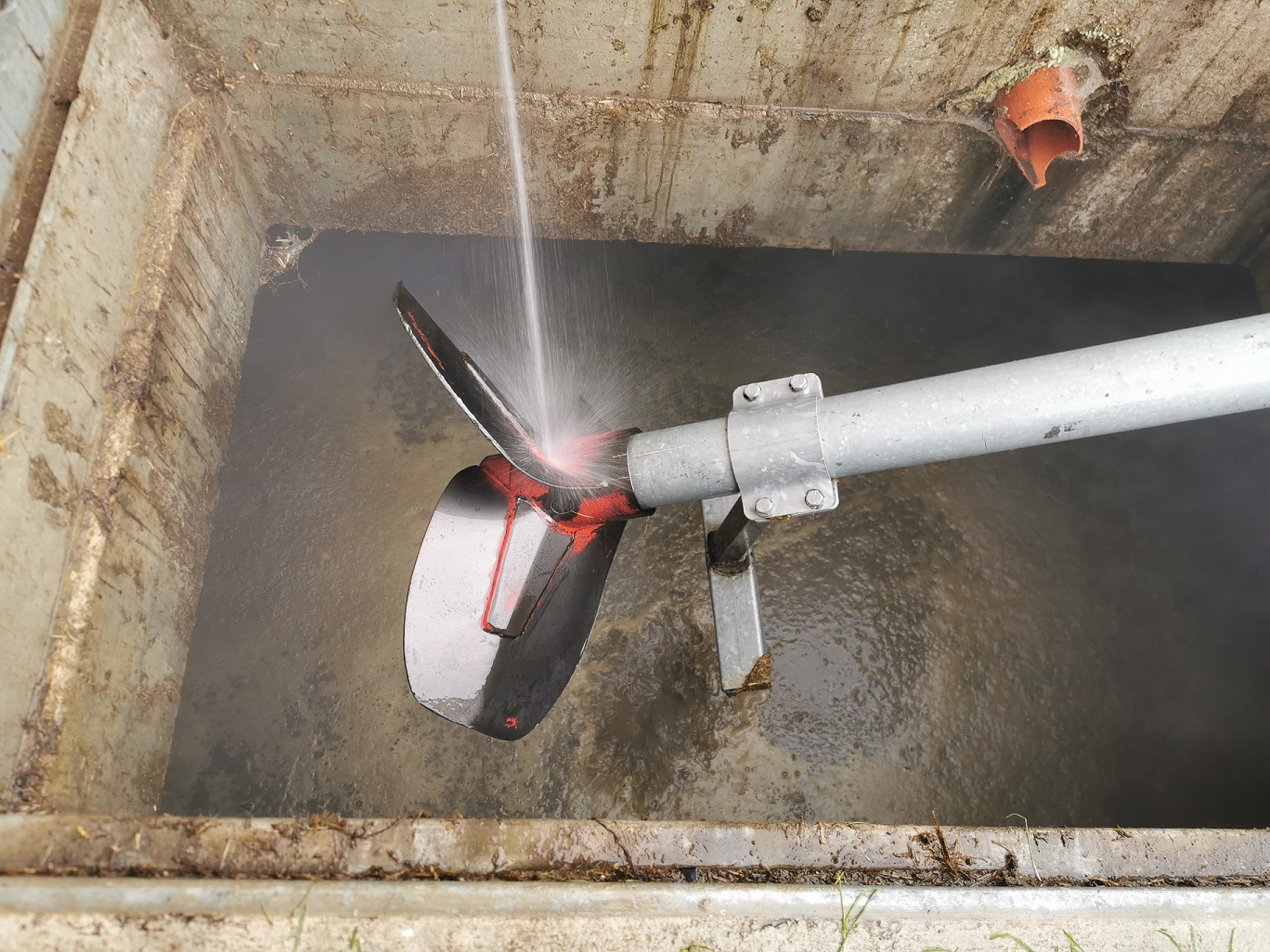
A current case from Austria shows how dangerous some seemingly harmless additives can be . A dairy farm in Tyrol with a state-of-the-art cubicle barn and a liquid manure storage half under the barn mixed elemental sulfur (25 kg/ha according to the label) into its pit. This corresponds to an amount of around 1.25 kg/m 3 of manure. Of the 160 m³ of liquid manure, around 100 m³ were then spread on the grassland areas on the same day. There were no incidents whatsoever. As is usual in practice, a slurry pit is not completely emptied and so the spreading of slurry began again about a month later. Approximately 20 minutes after the manure homogenization began, the farmer was faced with horror when he found his entire herd dead in his stable.
What had happened? Some of the gases, especially H 2 S hydrogen sulfide, had dissolved in the manure. By adding elemental sulfur a month ago, the sulfur content in the manure was further increased. The microorganisms in the manure further process it into sulfate, which is responsible for the formation of hydrogen sulfide. When the manure was homogenized, the harmful gases were released. These “manure gases” flowed out of the manure pit due to the resulting turbulence. Due to the direct connections to the stable via the manure discharge zone with a metal cover, the harmful gases were able to spread into the stable. This led to the death of the entire herd after a very short time. The farmer himself had entered the stable, saw the dead animals, understood the situation correctly and was able to escape outside at the last second. During subsequent gas measurements by the fire brigade, H 2 S levels of over 2000 ppm were found. The measurements by the HBLFA Raumberg-Gumpenstein a month later also showed no change. The contamination was still well over 1000 ppm. Due to this incident, a small-scale test was set up at the HBLFA Raumberg-Gumpenstein.
Limit values for H 2 S:
- In stables a maximum of 5 ppm
- From 200 ppm onwards, the first paralysis of the olfactory receptors occurs
- From 700 ppm the first respiratory paralysis
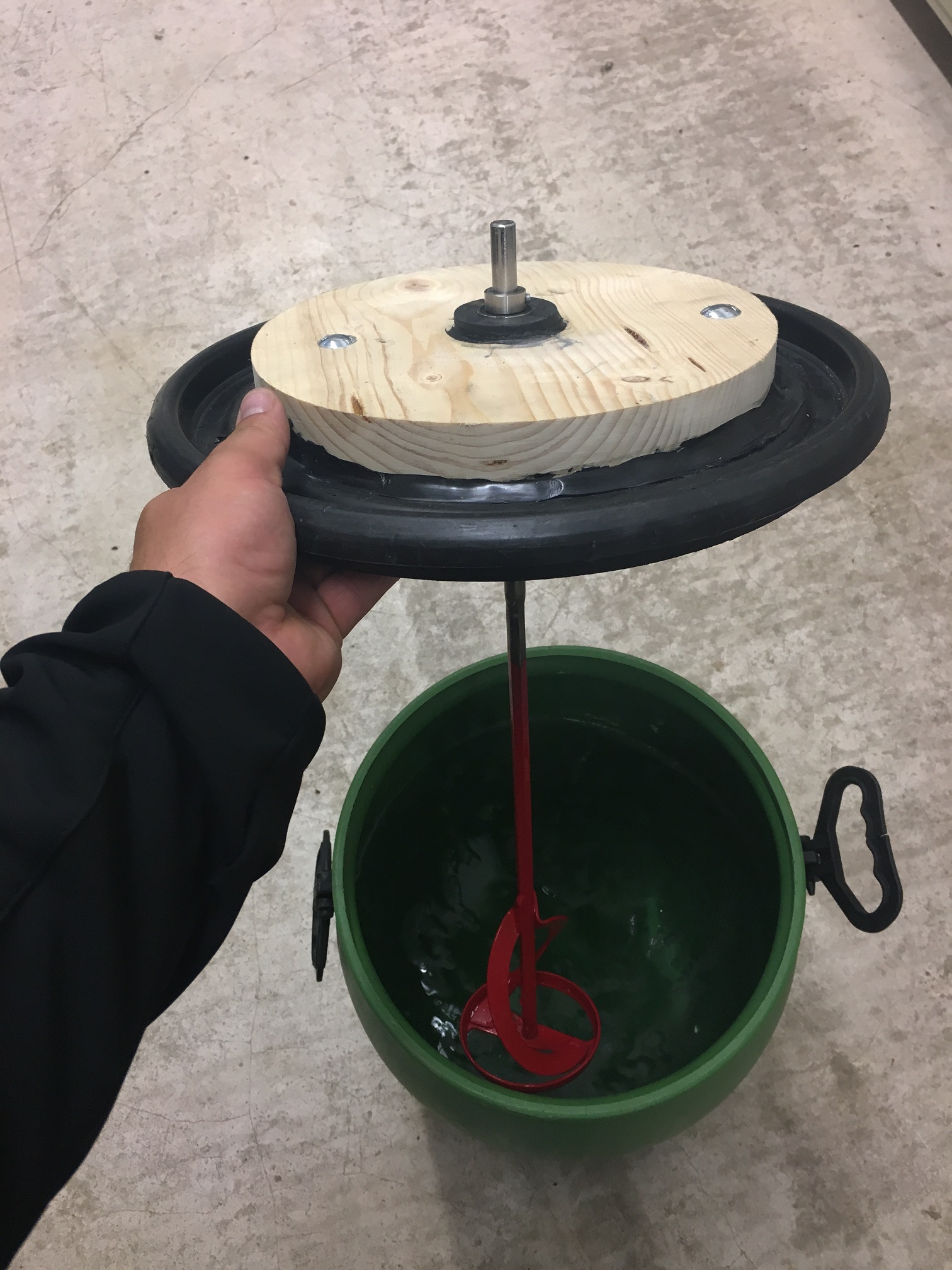
Small-scale experiment at the HBLFA Raumberg-Gumpenstein
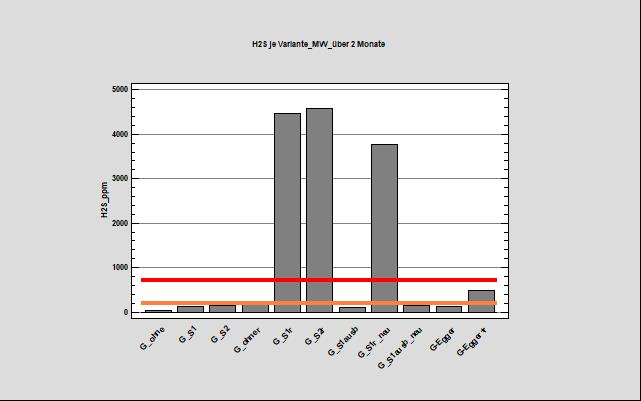
60 liter barrels were filled with manure and mixed with different application rates (1.25 and 2.0 kg/m3 of manure) of elemental sulfur. Three barrels of each variant were filled to ensure enough repetitions. The individual variants were then measured using a gas measuring device twice a week over a period of 2 months. All variants to which elemental sulfur was added and which were homogenized should be highlighted (G_S1r; G_S2r; G_S1r_neu). On average, these show significantly increased H 2 S loads over the two-month measurement period, sometimes rising to 4500 ppm. It should also be noted that untreated manure also tends to form hydrogen sulphide, up to the exposure limit of approx. 200 ppm.
What should you do?
Liquid fertilizers are an extremely complicated medium that cannot be standardized. This means that it is not possible to make general and always valid statements about which substances or gases are produced when manure additives are added, regardless of whether they are used as fertilizer or to combat emissions. In this case, the addition of elemental sulfur showed how quickly a harmful gas such as hydrogen sulfide can form. Since manure stores are not emptied completely at once, but are usually spread over several days (depending on the weather) or the manure is divided into several doses, it must be homogenized frequently. This can lead to serious incidents, which can hopefully be avoided in the future by using tested and correctly used manure additives.